
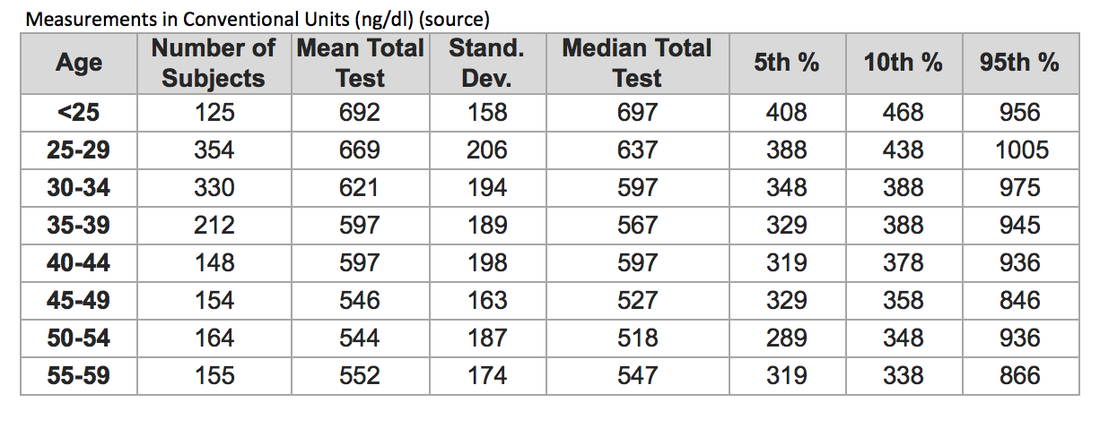
Mean serum levels of dioxin congeners in the hotspot group were 1.5–11.3 times higher than the non-sprayed group depending on specific compound.

We compared serum levels of dioxin, steroid hormones and prostate specific antigen (PSA) in men aged 56–81 years from herbicide-exposed hotspots ( n = 50) with those from non-sprayed regions ( n = 48). We therefore explored associations among dioxins, steroid hormones, age and prostate cancer risk in men. We discuss the practical meaningfulness of the effect sizes we estimate in relation to known factors (e.g., aging, geographic population) that influence men’s T concentrations.Īlthough Vietnam's massive herbicide exposure in 1960s and 1970s was clearly injurious to health, not all causal relationships have been clarified. Furthermore, men more oriented toward pair-bonding or offspring investment had lower T. We confirm that pair-bonded men have lower T than single men, and fathers have lower T than childless men. We meta-analyzed 114 effects from 66 published and unpublished studies covering four predictions inspired by the Challenge Hypothesis. However, the magnitude of these effects, and the influence of methodological variation on effect sizes, have not been quantitatively assessed.
It predicts that males pursuing mating opportunities have higher T than males pursuing paternal strategies, and in humans, many studies indeed report that men who are fathers and/or pair-bonded have lower T than childless and/or unpaired men. The Challenge Hypothesis provides a framework for understanding these life-history trade-offs via the disparate roles of testosterone (T) in aggression, sexual behavior, and parenting. Males of many species must allocate limited energy budgets between mating and parenting effort.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
